
دسته بندی سایت
محبوب ترین ها
پرفروش ترین ها
پر بازدید ترین های فورکیا
 فروش فیلتر بورسی استریکلی فقط 75 هزار تومان
فروش فیلتر بورسی استریکلی فقط 75 هزار تومان کسب درآمد اینترنتی 300000 تومان در خانه در کمتر از 30 دقیقه
کسب درآمد اینترنتی 300000 تومان در خانه در کمتر از 30 دقیقه روش درآمدزایی در خواب (تعجب نکنید! کلیک کنید و بخوانید)
روش درآمدزایی در خواب (تعجب نکنید! کلیک کنید و بخوانید) ربات همه کاره اینستاگرام
ربات همه کاره اینستاگرام کسب و کار اینترنتی با درآمد میلیونی
کسب و کار اینترنتی با درآمد میلیونی كسب درآمد اينترنتي روزانه حداقل100هزار تومان تضميني
كسب درآمد اينترنتي روزانه حداقل100هزار تومان تضميني کسب درآمد ابدی و بی نهایت 100% واقعی
کسب درآمد ابدی و بی نهایت 100% واقعی کسب درآمد روزانه حداقل یک میلیون تومان ! کاملا حلال و واقعـی !!
کسب درآمد روزانه حداقل یک میلیون تومان ! کاملا حلال و واقعـی !! مجموعه ی آموزش تعمیر لامپ کم مصرف (از مبتدی تا پیشرفته)
مجموعه ی آموزش تعمیر لامپ کم مصرف (از مبتدی تا پیشرفته) افزایش ممبر کانال، گروه و ربات تلگرام به صورت بی نهایت (اد ممبر)
افزایش ممبر کانال، گروه و ربات تلگرام به صورت بی نهایت (اد ممبر) دانلود پکیج درآمدزایی 400هزارتومن در 40دقیقه (مخصوص شرایط کرونا)
دانلود پکیج درآمدزایی 400هزارتومن در 40دقیقه (مخصوص شرایط کرونا) آموزش بازكردن انواع قفل ها بدون كليد(ويژه)
آموزش بازكردن انواع قفل ها بدون كليد(ويژه) کسب و کار اینترنتی در منزل
کسب و کار اینترنتی در منزل آموزش برنامه نویسی آردوینو
آموزش برنامه نویسی آردوینو دانلود مجموعه آموزشی پایپینگ ( Piping ) و نقشه خوانی + آموزش سه نرم افزار طراحی و تحلیل لوله کشی صنعتی
دانلود مجموعه آموزشی پایپینگ ( Piping ) و نقشه خوانی + آموزش سه نرم افزار طراحی و تحلیل لوله کشی صنعتی بازگردانی پیامک های حذف شده- ریکاوری پیامک ۱۰۰٪ عملی
بازگردانی پیامک های حذف شده- ریکاوری پیامک ۱۰۰٪ عملی آموزش رایگان کسب درآمد از سایت الیمپ ترید ( olymp trade )
آموزش رایگان کسب درآمد از سایت الیمپ ترید ( olymp trade ) اموزش ویرایش امضا و پکیج برنامه اندروید و کسب درامد از مارکت های اندرویدی
اموزش ویرایش امضا و پکیج برنامه اندروید و کسب درامد از مارکت های اندرویدی کد های آماده html و css جهت یادگیری و طراحی سریع
کد های آماده html و css جهت یادگیری و طراحی سریع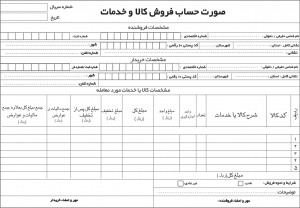 دانلود نمونه فاکتور آماده با فرمت ورد - اکسل و عکس
دانلود نمونه فاکتور آماده با فرمت ورد - اکسل و عکس آموزش ساخت بازی بدون دانش برنامه نویسی و طراحی سه بعدی مبتدی تا پیشرفته با نرم افزار
آموزش ساخت بازی بدون دانش برنامه نویسی و طراحی سه بعدی مبتدی تا پیشرفته با نرم افزار آموزش كامل تعمير لامپ كم مصرف(اختصاصي)
آموزش كامل تعمير لامپ كم مصرف(اختصاصي) اموزش کسب درامد از اینترنت روزانه ۳میلیون تومان تضمینی و تست شده
اموزش کسب درامد از اینترنت روزانه ۳میلیون تومان تضمینی و تست شده نسخه خطی اشعار و پیشگویی های شاه نعمت الله ولی
نسخه خطی اشعار و پیشگویی های شاه نعمت الله ولی نسخه خطی اشعار و پیشگویی های شاه نعمت الله ولی
نسخه خطی اشعار و پیشگویی های شاه نعمت الله ولی درامدزایی در خواب! (تعجب نکنید! بخوانید)
درامدزایی در خواب! (تعجب نکنید! بخوانید)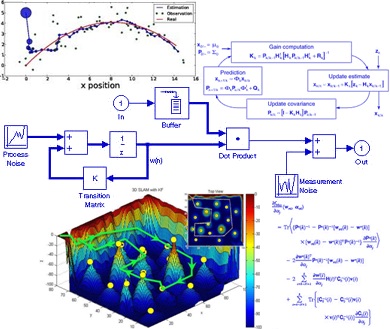 دانلود پاورپوینت فیلتر کالمن بر روی یک سنسور شتاب سنج برای تخمین سه متغیر حالت
دانلود پاورپوینت فیلتر کالمن بر روی یک سنسور شتاب سنج برای تخمین سه متغیر حالت مدار داخلی واکی تاکی(اموزش ساخت)
مدار داخلی واکی تاکی(اموزش ساخت) کتاب افزایش ممبر کانال تلگرام
کتاب افزایش ممبر کانال تلگرامبرچسب های مهم
آمار بازدید سایت
پیوند ها
مقاله 2015 به همراه ترجمه حرفه ای
نمونه کار از صفحه اول مقاله در ذیل قابل مشاهده است.
تعداد صفحات اصل مقاله: 14 صفحه
ترجمه: 29 صفحه
Analytical Fault Tolerance Assessment and Metrics for TSV-Based 3D Network-on-Chip
Abstract——Reliability is one of the most challeng in gproblemsin the context of three-dimensional network-on-chip (3DNoC) systems. Reliability analysis is prominent for early stages of the manufacturing process in order to prevent costly redesigns of a target system. This article classifies the potentialphysical faults of a baselineTSV-based 3D NoC architecture by targeting two-dimensional (2D) NoC components and theirinter-die connections. In this paper, through-siliconvia (TSV) issues, thermal concerns, and single event effect (SEE) are investigated and categorized, inorder to propose evaluation metrics for inspecting the resiliency of 3D NoC designs. A reliability analysis for major source of faults is reported in this article separately based on theirmeantime to failure (MTTF). TSV failure probability induced by inductive and capacitive coupling is also discussed. Finally, the paper provides a formal reliability analysis on the aggregated faults that affect TSV. This formal analysis is critical for estimating there siliency of different components in order to mitigate the redundancy cost of fault-tolerant design or to examine the efficiency of any proposed fault-tolerant methods for 3D NoC architectures.
Index Terms—Reliability analysis, 3D NoC, TSV, thermal, SEE, fault
1 INTRODUCTION
Technology scaling, improving transistor performance with higher frequency, designing novel architectures, and reducing energy consumed per logic operation have become essential for improving the computational performance by orders of magnitude. Furthermore, energy efficiency is of great importance for both future supercomputers and embedded systems [1]. Reliability is another significant challengeof singlechip designers as petascale computational performance comes to fruition, by targeting exascale systems for the next decade [2]. Increasing power consumption, power variation, and power density have negative impacts on reliability of on-chip designs. Rapid changes in power consumption,uncoverson-chipvoltagefluctuationsandconsequently leads to transient errors. High temperatures also increase leakage power consumption, resulting in a self-reinforcing cyclic dependency between power and temperature [3, p. 25]. On the other hand, higher chip temperatures may be derived from high temporal and spatial power densities. Power consumption and consequently temperature have adirectrelationshipwiththereliabilityofsystems[4]. With technology and design scaling slowing down, the processor industry is rapidly moving from a single core with high-frequency designs to many-core chips. Threedimensional (3D) integration instead of two-dimensional (2D) integration is another trend to keep the traditionally expected performance improvements. These computational processors and memories, or intellectual properties (IPs) in
general, need robust, high performance and low power interconnections. Over the years, system integration has reached a stage where a complete system can be integrated onto a single chip. As system-on-chip (SoC) design expands to encompass ever-increasing cores to meet the high performance needs, it has become clear that traditional bus-based systems do not provide scalability and efficiency in interconnecting large number of cores on a chip. Network-onchip (NoC) has been proposed as a scalable and efficient interconnection for future systems [5].
چکیده
قابلیت اطمینان یکی از چالش برانگیز ترین مشکلات در زمینه شبکه روی تراشه سیستم های سه بعدی (3DNOC) است. اهمیت تجزیه و تحلیل قابلیت اطمینان در جلوگیری از طراحی دوباره و پر هزینه یک سیستم هدف در مراحل اولیه فرآیند تولید است. این مقاله خطاهای فیزیکی بالقوه یک معماری NoC سه بعدی خط مبنای مبتنی بر TSV را با هدف قرار دادن مولفه های NoC دو بعدی و ارتباطات درون قالب آن طبقه بندی می کند. در این مقاله، از طریق مسائل سیلیکونی (TSV) مسائل حرارتی و اثر رویداد منفرد ( SEE) مورد بررسی قرار گرفته و طبقه بندی شده تا معیارهای ارزیابی برای بازرسی حالت ارتجاعی طرح NOC سه بعدی ارائه شود. تجزیه و تحلیل قابلیت اطمینان برای منبع اصلی خطاها نیز در این مقاله به طور جداگانه بر اساس متوسط زمان آن ها (MTTF) گزارش شده است .شکست TSV احتمالی از جفت القایی و خازنی نیز بحث شده است. در نهایت این مقاله قابلیت اطمینان رسمی تجزیه و تحلیل درباره خطاهای جمع آوری شده که بر TSV تاثیر می گذارد را فراهم می کند .این تجزیه و تحلیل رسمی برای تخمین حالت ارتجاعی اجزای مختلف به منظور کاهش هزینه افزونگی در طراحی مقاوم در برابر خطا و یا برای بررسی بهره وری روش های مقاوم در برابر خطای پیشنهادی برای معماری NOC سه بعدی حیاتی است.
کلمات کلیدی - تجزیه و تحلیل قابلیت اطمینان، NOCسه بعدی، TSV، حرارتی، SEE، خطا
مبلغ واقعی 75,000 تومان 10% تخفیف مبلغ قابل پرداخت 67,500 تومان
برچسب های مهم